姓名:陳玟君,指導教授:莊程豪
Abstract
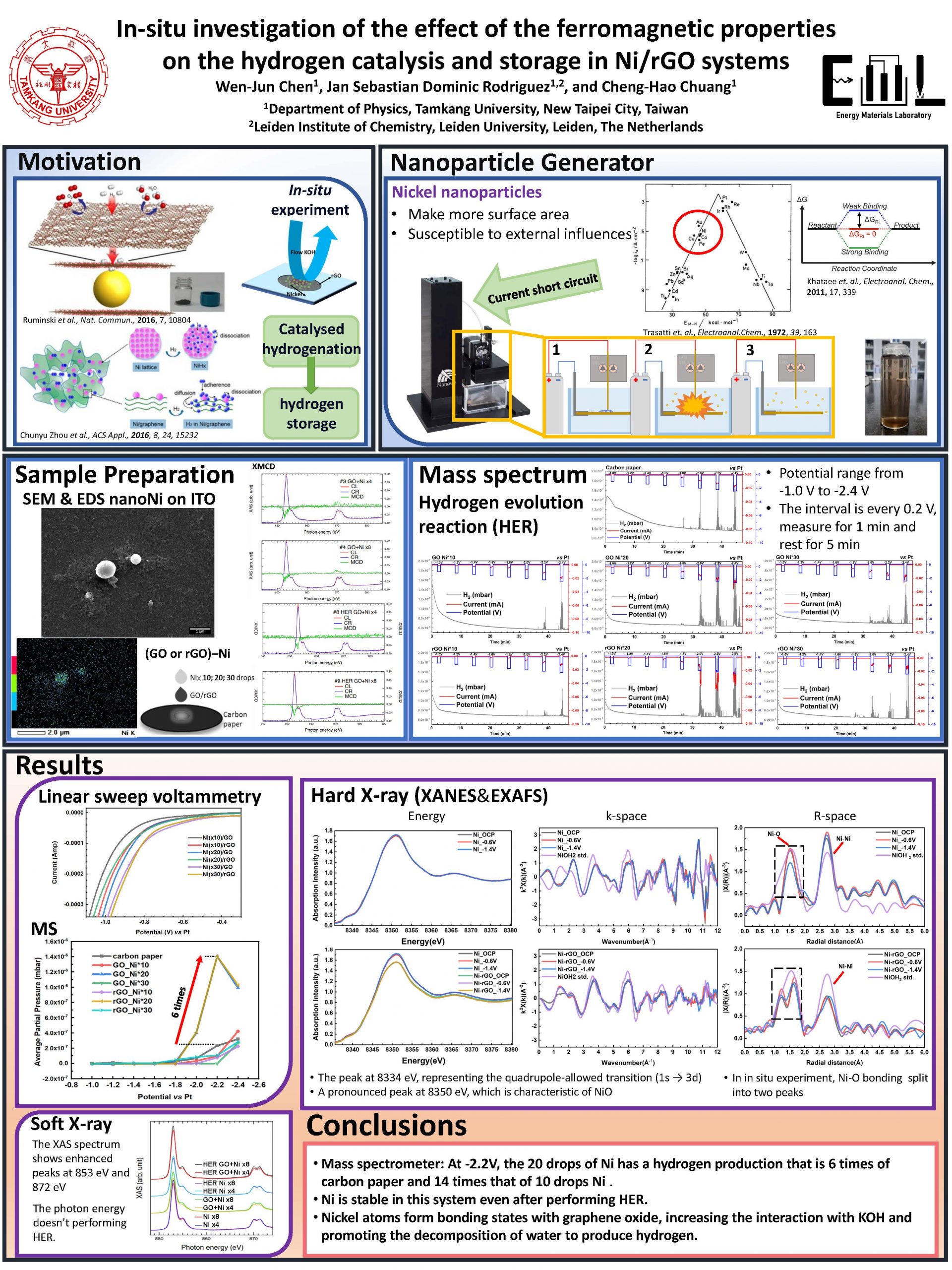
Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) can store hydrogen when composited with catalytic materials, such as nickel (Ni), which has shown ferromagnetic properties. Our study combines these two materials to capture hydrogen and explore the relationship between magnetism and catalysis. In our sample synthesis, we employed a straightforward method to form rGO membranes (via drop-casting and electroreduction methods), and subsequently deposited Ni nanoparticles via drop-casting. Sample identification is performed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to analyze the surface morphology and the chemical characteristics of the material. Energy dispersion spectrometer (EDS) measurement was used to calculate and observe the sample’s composition. Finally, we will explore whether this composite material can capture and store the produced hydrogen and the effects of hydrogen production. In our future work, we will perform X-ray Magnetic Circular Dichroism (XMCD) to observe whether adding an external magnetic field affects the hydrogen production and storage performances of Ni/rGO materials.
